
Designed by Freepik.com
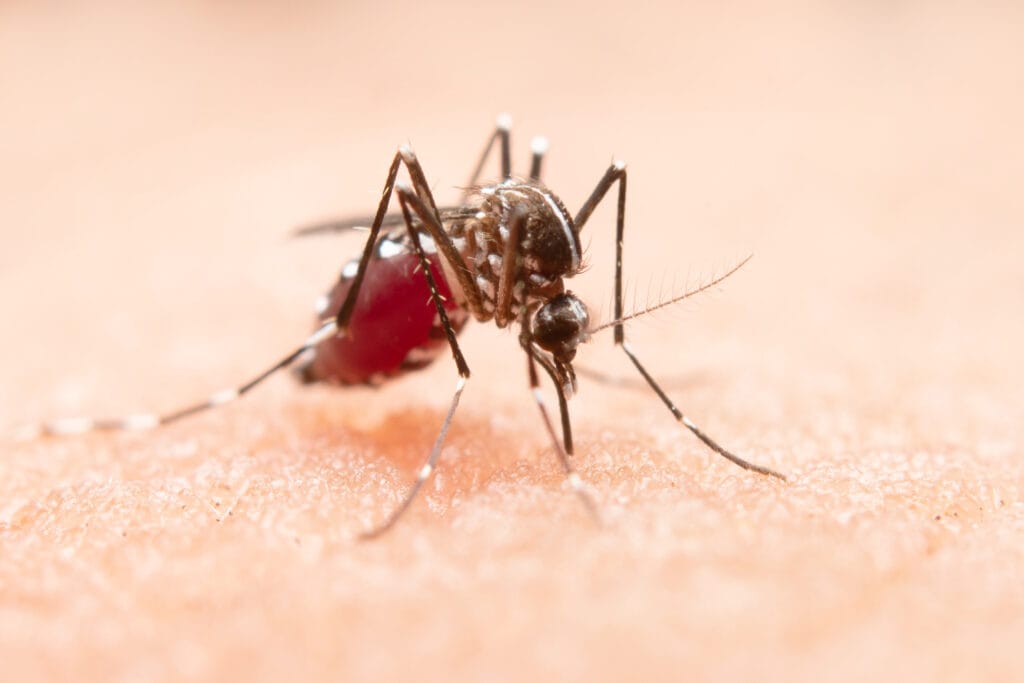
“Disease X” – As the death toll climbs and scientists race against time, this “unknown killer” is sparking fears of a pandemic worse than COVID-19. Here’s what you need to know—and how to stay safe. In late October 2024, a severe malaria outbreak emerged in the Panzi health zone of Kwango Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Initially referred to as “Disease X” due to its unknown nature, the illness has since been identified as a severe form of malaria, exacerbated by malnutrition and respiratory complications.
Timeline and Identification:
October 2024: Reports of a mysterious illness with symptoms including fever, headache, cough, and runny nose surfaced in the Panzi health zone. The disease primarily affected children under 14, many of whom were severely malnourished.
Early December 2024: The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) dispatched teams to the affected region to investigate. Initial rapid tests indicated malaria in some cases. The Sun
December 17, 2024: The DRC’s health ministry confirmed that the outbreak was due to a severe form of malaria, compounded by malnutrition and respiratory illnesses. Wikipedia
Transmission and Origin:
Malaria is transmitted through the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. In this outbreak, there is no evidence to suggest zoonotic transmission (i.e., from animals to humans).
Pathogen Structure and Identification:
The causative agent is Plasmodium falciparum, a protozoan parasite responsible for the most severe form of malaria. Microscopic examination of blood smears and rapid diagnostic tests have been utilized to identify the parasite in affected individuals.
Precautions and Prevention:
To reduce the risk of malaria infection:
- Use Insecticide-Treated Nets (ITNs): Sleeping under ITNs can significantly reduce mosquito bites.
- Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS): Applying insecticides to indoor walls can kill mosquitoes that rest there.
- Antimalarial Medications: In high-risk areas, prophylactic antimalarial drugs may be recommended.
- Eliminate Standing Water: Removing stagnant water sources can reduce mosquito breeding sites.
Virulence and Comparison to COVID-19:
While malaria is a serious and potentially fatal disease, it is not transmitted person-to-person like COVID-19. The current outbreak’s high mortality rate is largely attributed to severe malnutrition among the affected population, which exacerbates the disease’s severity.
Ongoing Research and Treatment:
Health authorities are focusing on distributing antimalarial medications and addressing malnutrition in the affected regions. Standard antimalarial treatments, such as artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs), are effective against Plasmodium falciparum. Efforts are also underway to improve diagnostic capabilities and healthcare access in remote areas.
Current Impact and Affected Areas:
As of December 17, 2024, the outbreak has resulted in at least 143 deaths and 592 confirmed cases, primarily in the Panzi health zone of Kwango Province. The disease has also spread to neighboring regions, including Katenda and parts of Mai-Ndombe Province. Wikipedia
Recent Research Publications:
For in-depth information, consider the following articles:
- “Disease X in the Tropics: Preventing the Next Pandemic” This article discusses the potential impact of unknown pathogens and emphasizes the importance of preparedness in tropical regions. Frontiers
- “Disease X: A Looming Threat and a Call for Preparedness” This communication highlights the threat of Disease X and advocates for enhanced global preparedness efforts. Lippincott Journals
- “Could the Next ‘Disease X’ Be a Pandemic of Virus-Induced…” This article explores potential global public health threats, considering worst-case scenarios of pandemics caused by unknown pathogens. Taylor & Francis Online
These resources provide valuable insights into the challenges of emerging infectious diseases and the importance of global health preparedness.
Recent Developments in Congo’s Disease Outbreak
The Sun: Mystery ‘Disease X’ ripping through Congo finally identified after 143 deaths and 592 cases
For Homepage, click here




